-
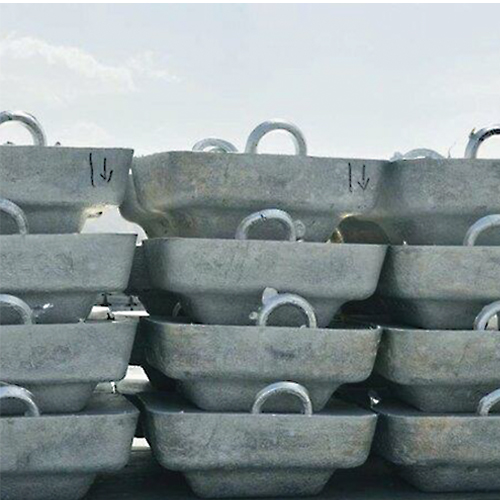
A thousand pound ingot
Aluminum ingots are non-ferrous product that is produced by pouring molten aluminum into special molds. These molds come in a variety of sizes and shapes, and the ingots created by this variety have different types in appearance. Today, aluminum is the second most widely used metal in the world after iron. The widespread use of this metal in various industries has led to special attention to its identification and extraction from existing mines in the country.
-
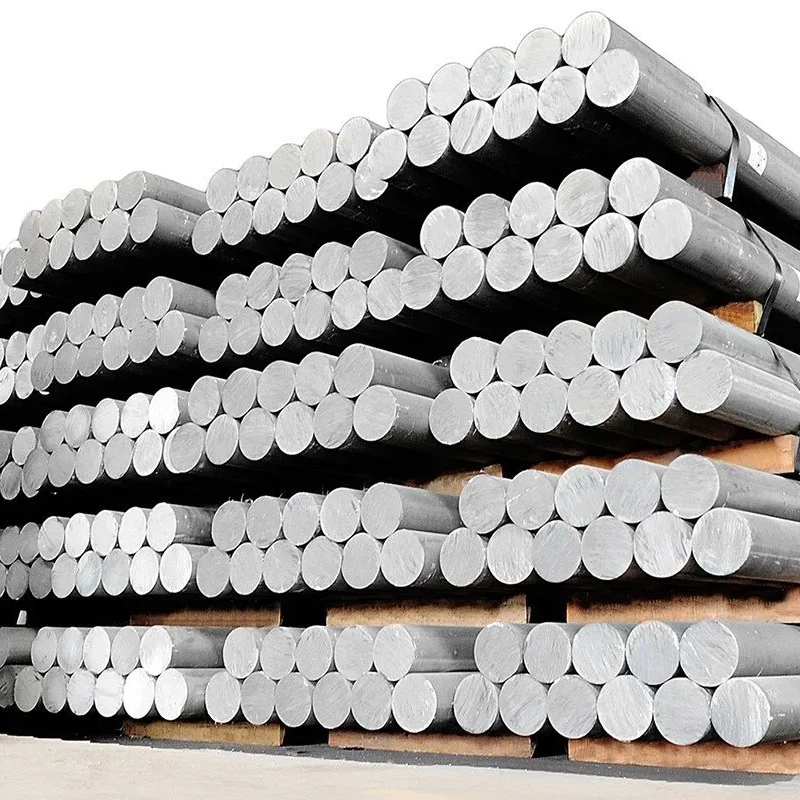
Aluminium billets
Aluminum Billet is one of the semi-finished products of aluminum casting, which is obtained from aluminum ingot. This product is produced according to the industries and the application of the customer’s order in various usable alloy groups according to international standards with different diameters. In this collection, the billets are produced in diameters of 6 to 12 inches by the Air slip method.
-
EPS (Expandable polystyrene)
Polystyrene is one of the petrochemical products widely used in various industries, which is produced through the polymerization of monomer styrene. Expandable polystyrene (EPS) is one type of this polymer characterized by its increase in volume when exposed to heat. This expandability is caused by the uniform distribution of a hydrocarbon agent, like pentane, within the EPS structure. Manufacturers can expand the beads inside molds of different shapes to obtain a plastic object of the same shape.
-
GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene)
Undoubtedly, one of the most special chemical chains in the industrial and petrochemical markets is polystyrene, which is sold in resistant and ordinary types. Ordinary polystyrene is also known as GPPS. Butadiene rubber, ordinary oil, and styrene are the three main components of making ordinary polystyrene.
The production and manufacture of disposable containers is one of the most important uses of ordinary polystyrene. The production of household and sports equipment is one of the many other advantages of this polymer.
-
HDPE (High Density Polyethylene)
Heavy polyethylene (High density polyethylene) is a high density type of polyethylene and has good strength and resistance against impact, sunlight, chemicals, etc. This material is widely used in the production of pipes, bottles, etc. HDPE has different grades, each of which has unique properties based on the intended use.
-
Homopolymer
Among the properties and practical features of Homo-Polymer, we can mention high adhesion to different surfaces, favorable flexibility, ability to mix with various fillers and organic solvents, as well as the formation of a transparent and colorless film after drying.
Homopolymer is mainly used in wood glue, packaging glue, machine carpets, carpets, and fabric. Because polyvinyl acetate adhesives have good resistance to oil, grease, and acid. Adhesives based on this resin are environmentally friendly and do not pose health risks.
-
LLDPE (Linear Low Density Polyethylene)
Linear light polyethylene or LLDPE for short has a density between 0.915-0.925 g/cm3. It is a linear polymer that has short branches and is generally produced by copolymerization with short-chain alpha olefins such as 1-butene, 1-hexene, and 1-octene.
Compared to LDPE, LLDPE has higher tensile strength and also has higher impact and puncture resistance. -
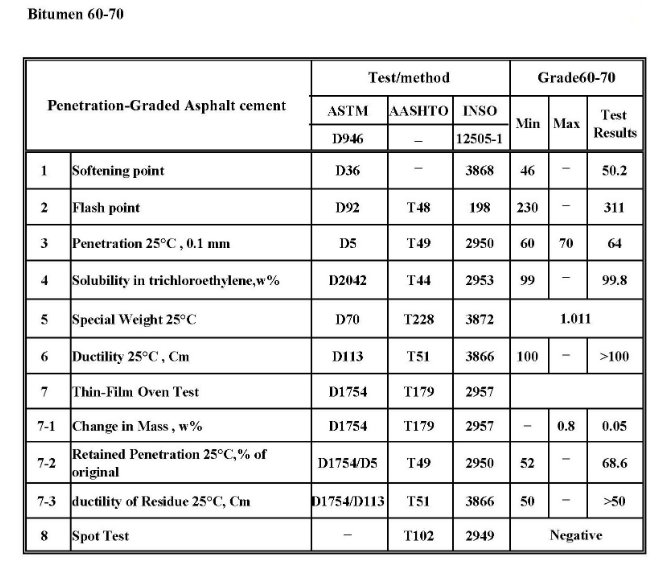
Penetration Graded Bitumen
Penetration Grade Bitumen is a standard bitumen usually used as a Paving Grade Bitumen essential for road construction and for the production of asphalt pavements with superior properties, and it’s very important once it bounds the aggregates and creates a unique cohesion and stability to the bituminous mix.
-
Performance Graded Bitumen
Performance Grade (PG) Bitumen is bitumen which is graded based on its performance at different temperatures. In the Superpave grading system, binders are classified according to their performance in extreme hot and cold temperatures and are called performance grade (PG) bitumen. The main purpose of grading and selecting asphalt binders using the PG system is to make certain that the binder has the appropriate properties for environmental conditions in the field. PG asphalt binders are selected to meet expected climatic conditions as well as traffic speed and volume adjustments. Therefore, the PG system uses a common set of tests to measure the physical properties of the binder that can be directly related to the field performance of the pavement at its service temperatures by engineering principles. It is one of the most important changes introduced in Super Pave that acceptance limits are the same but have to be met at specific pavement temperatures and traffic conditions.
-
Random copolymer
Polypropylene random copolymers are thermoplastic resins produced through the polymerization of propylene, with ethylene or butene bonds introduced in the polymer chain. The resins provide a broad range of characteristics and are used in a wide range of applications. -
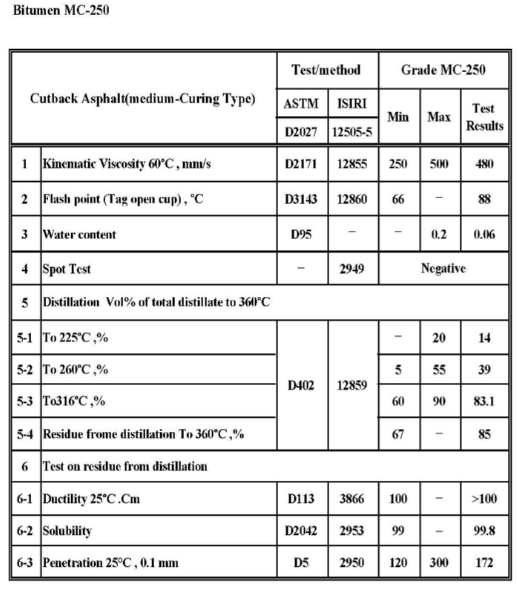
Soluble Graded Bitumen
Soluble bitumen is a mixture of bitumen and a suitable solvent (e.g. kerosene or gasoline). The type and quality of soluble bitumen depend on the quality of the original pure bitumen, the type of solvent, and the amount of solvent. This bitumen is liquid at room temperature or liquefied with a little heat.
Soluble bitumen is used in various types of paving asphalts. The setting or hardening rate of this type of bitumen depends on the type of solution.
Lack of access to bitumen heating equipment, decomposition of bitumen at high temperatures, cooling of bitumen during operation, the impossibility of its penetration into porous minerals, the need for workers’ safety, fire, and time-consuming cause soluble bitumen to be used in some cases.
Soluble bitumen is used in road construction for surface coatings, infiltration, cold factory asphalt, or on-site mixes.